Integer浅析-JDK1.8
java.lang.Integer浅析
源码分析环境
- OS: Ubuntu 16.04 LTS X64
- IDE: IDEA 2017.1.3
- JDK:
- HotSpot™ 64-Bit JDK1.6
- HotSpot™ 64-Bit JDK1.7
- HotSpot™ 64-Bit JDK1.8
- OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.131-b11, mixed mode) OpenJDK1.8
一. Integer类的声明
public final class Integer extends Number implements Comparable<Integer>{}
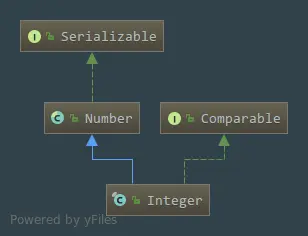
- Integer是一个 final 类,也就是不可变的类。
- 继承了 Number 这个抽象类,拥有了父类的一系列方法,同时也隐式的实现了 Serializable 接口。
- 实现了 Comparable 接口,说明它是可以进行比较的,可以与其他Integer对象进行比较。 使用泛型确保了compareTo方法的类型安全。
二. 特殊的内部类
Java 自动缓存 - 128 到 127 之间的整数,这个缓存将会在第一次使用时被初始化,缓存的大小受 JVM 运行参数 -XX:AutoBoxCacheMax=<size>控制,可以通过这个进行更改。
private static class IntegerCache {
static final int low = -128;
static final int high;
static final Integer cache[];
static {
// high value may be configured by property
int h = 127;
String integerCacheHighPropValue =
sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");
if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) {
try {
int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue);
i = Math.max(i, 127);
// Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE
h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1);
} catch( NumberFormatException nfe) {
// If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it.
}
}
high = h;
cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1];
int j = low;
for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++)
cache[k] = new Integer(j++);
// range [-128, 127] must be interned (JLS7 5.1.7)
assert IntegerCache.high >= 127;
}
private IntegerCache() {}
}
直接上例子,默认情况下是这样的:
Integer integer1 = 127;
Integer integer2 = 127;
System.out.println(integer1 == integer2); // true
Integer integer3 = 128;
Integer integer4 = 128;
System.out.println(integer3 == integer4); // false
Integer integer5 = -128;
Integer integer6 = -128;
System.out.println(integer5 == integer6); // true
Integer integer7 = -129;
Integer integer8 = -129;
System.out.println(integer7 == integer8); // flase
然后如果我们还想让它缓存更大的数的话就给 JVM 设置一个运行参数,这里假如我设置到最大缓存到 256 ,-XX:AutoBoxCacheMax= 256
Integer integer1 = 256;
Integer integer2 = 256;
System.out.println(integer1 == integer2); // true
Integer integer3 = 257;
Integer integer4 = 257;
System.out.println(integer3 == integer4); // false 超过了最大缓存就比较地址了,没有缓存可以取了
三. Integer的属性
最小值
最小值是 2^-31 ,换算过来就是 - 2147483648 ,因为是个静态属性,可以直接通过 Integer.MIN_VALUE 取到
// A constant holding the minimum value an {@code int} can have, -2^31
@Native public static final int MIN_VALUE = 0x80000000;
最大值
最大值是2^31,换算过来就是2147483647,因为是个静态属性,可以直接通过Integer.MAX_VALUE取到。
// A constant holding the maximum value an int can have, 2^31-1.
@Native public static final int MAX_VALUE = 0x7fffffff;
类型
根据方法注释我们可以知道是 Integer 类型的 Type 是一个基本类型。
/**
* The Class instance representing the primitive type int.
* @since JDK1.1
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static final Class<Integer> TYPE = (Class<Integer>) Class.getPrimitiveClass("int");
然后我们这里就会引发一个疑问了,为什么 Integer 的 Type 会是 in.class 呢?,这里我们其实可以像个例子:
System.out.println(Integer.TYPE); // int
// 使用 == 进行比较
System.out.println(Integer.TYPE == int.class); // true
System.out.println(Integer.class == int.class); // false
// 如果还想更加准确地比较,可以使用System.identityHashCode()产生一个哈希码,这个是给予地址生成的,不是给予内容
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(Integer.TYPE)); // 2061475679
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(int.class)); // 2061475679
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(Integer.class)); // 410424423
这里我们可以很清楚的得到理论就是:
- Integer.TYPE 跟 int.class 是相等的,因为 Integer.TYPE 这个常量就是通过 Class.getPrimitiveClass(”int”) 得到的。
- Integer.class 跟 int.class 是不相等的,因为 Integer.class 是个包装类,我们可以看到它的源码, int.class 的源码不能直接在 JDK 中看到。
列举出所有可能作为数字的字母
列举出所有可能作为数字的字母,每个字母对应着 ASCII 码,是可以进行转换的,给方法内部使用的。
// All possible chars for representing a number as a String
final static char[] digits = {
'0' , '1' , '2' , '3' , '4' , '5' ,
'6' , '7' , '8' , '9' , 'a' , 'b' ,
'c' , 'd' , 'e' , 'f' , 'g' , 'h' ,
'i' , 'j' , 'k' , 'l' , 'm' , 'n' ,
'o' , 'p' , 'q' , 'r' , 's' , 't' ,
'u' , 'v' , 'w' , 'x' , 'y' , 'z'
};
四. 构造方法
- 传入一个 int 类型的值
public Integer(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
- 传入一个 String 类型的数字
public Integer(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
this.value = parseInt(s, 10);
}
五.Integer的方法
toString
重写了 Object 的 toString() 方法。
public static String toString(int i, int radix) {
if (radix < Character.MIN_RADIX || radix > Character.MAX_RADIX)
radix = 10;
/* Use the faster version */
if (radix == 10) {
return toString(i);
}
char buf[] = new char[33];
boolean negative = (i < 0);
int charPos = 32;
if (!negative) {
i = -i;
}
while (i <= -radix) {
buf[charPos--] = digits[-(i % radix)];
i = i / radix;
}
buf[charPos] = digits[-i];
if (negative) {
buf[--charPos] = '-';
}
return new String(buf, charPos, (33 - charPos));
}
toUnsignedString
转变成一个无符号的 String 类型。
public static String toUnsignedString(int i, int radix) {
return Long.toUnsignedString(toUnsignedLong(i), radix);
}
valueOf
- 传入一个文本型的数字转为 Integer 类型。
public static Integer valueOf(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
return Integer.valueOf(parseInt(s, 10));
}
- 手动装箱,把一个基本数据类型转为包装类型
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
return new Integer(i);
}
转换为基本数据类型
public byte byteValue();
public short shortValue();
public int intValue();
public long longValue();
public float floatValue();
public double doubleValue();
equals
首先不是 Integer 类型就直接不相等,否则直接比对值。
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Integer) {
return value == ((Integer)obj).intValue();
}
return false;
}
String 转 Integer
Integer getInteger(String nm);
Integer getInteger(String nm, int val);
Integer getInteger(String nm, Integer val);
Integer decode(String nm);
Integer valueOf(String s);
Integer valueOf(String s, int radix);
````
### String 转基本类型
```java
int parseUnsignedInt(String s);
int parseUnsignedInt(String s, int radix);
int parseInt(String s);
int parseInt(String s, int radix);
compareTo
跟另外一个 Integer 类型比较。
public int compareTo(Integer anotherInteger) {
return compare(this.value, anotherInteger.value);
}
六.静态方法
compare
- 传入两个 int 类型的数字进行比较
public static int compare(int x, int y) {
return (x < y) ? -1 : ((x == y) ? 0 : 1);
}
- 传入两个无符号类型的数字进行比较
public static int compareUnsigned(int x, int y) {
return compare(x + MIN_VALUE, y + MIN_VALUE);
}
toUnsignedLong
转换为 Long 类型无符号
public static long toUnsignedLong(int x) {
return ((long) x) & 0xffffffffL;
}
sum
对两个数求和
public static int sum(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
max
比较 2 个数,并返回最大数(JDK1.8 )
public static int max(int a, int b) {
return Math.max(a, b);
}
min
比较两个数,并返回最小的那个数(JDK1.8 )
public static int min(int a, int b) {
return Math.min(a, b);
}